12/11/2025
In automotive controllers, the two most widely used main chips are MCUs and SoCs. Traditional vehicles mainly rely on MCUs, while intelligent vehicles, driven by increasing functional complexity, are gradually adopting SoCs. In domain controllers, an MCU + SoC hybrid architecture is commonly used. So what exactly are the differences between an MCU and a SoC?
MCU stands for Microcontroller Unit. It is also known as a single-chip microcontroller. The well-known 8051 microcontroller studied in universities is a classic example of an MCU.
A microcontroller (Single Chip Microcomputer) originates from the architecture of traditional microcomputers. A conventional microcomputer consists of:
These components are usually implemented using multiple independent chips connected via external buses on a motherboard. This structure allows flexible configuration but increases complexity, size, and power consumption.
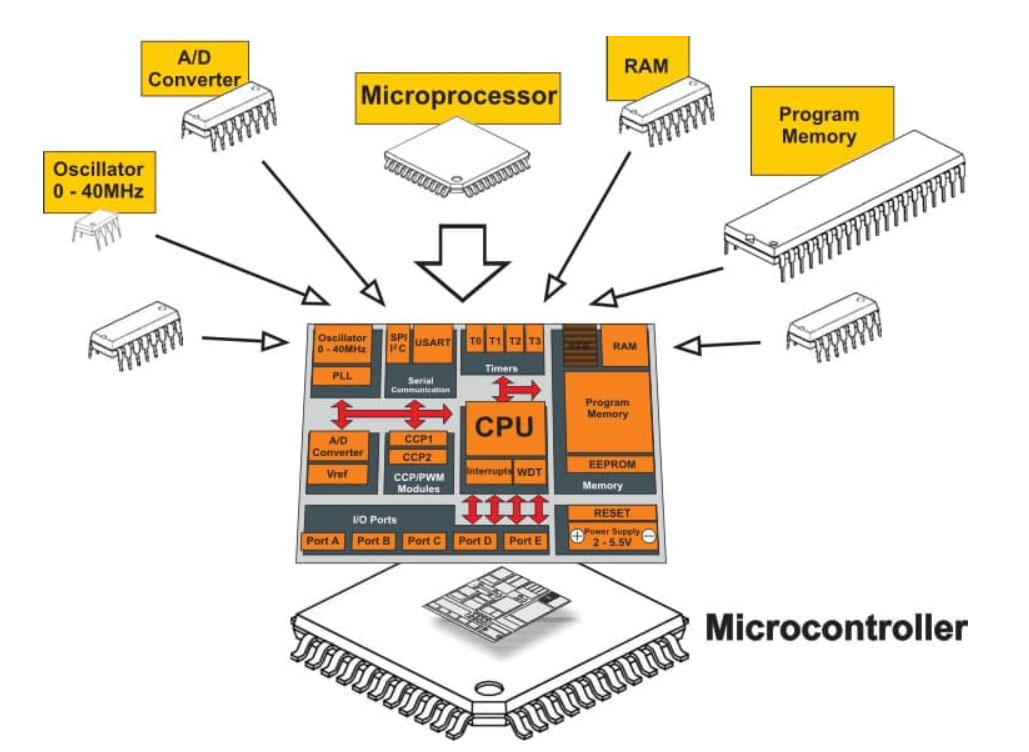
An MCU integrates the CPU, memory, and I/O peripherals into a single chip, enabling all data processing and control operations to be completed internally. This results in:
An MCU typically includes:
In automotive MCUs, additional dedicated peripherals are often integrated, such as:
As vehicles evolve toward electrification and intelligence—covering digital dashboards, infotainment systems, T-Box connectivity, and domain controllers—traditional MCU expansion through simple peripherals is no longer sufficient. This drives the adoption of SoCs.
SoC (System on Chip) refers to integrating multiple functional modules into a single chip, forming a system close to a complete computer.
Although both MCUs and SoCs are single-chip solutions, their design goals differ fundamentally:
This difference in goals leads to substantial architectural differences.
MCUs usually feature:
SoCs, on the other hand, adopt heterogeneous multi-core architectures, including:
A typical example is a smartphone SoC such as Qualcomm Snapdragon 865, which integrates multiple Cortex-A cores and a high-performance GPU.
Although some automotive MCUs now adopt multi-core designs, they still differ significantly from SoCs in performance scale and system complexity.
MCUs prioritize real-time response. Many MCU-based systems operate in:
Startup time is typically tens of milliseconds, meeting strict automotive requirements such as fast wake-up (<100 ms) and safety-critical response times (e.g., emergency braking within 200 ms).
SoCs are optimized for multi-tasking and high computational performance and usually run:
However, these operating systems require longer startup times—often several seconds or more—making them unsuitable for certain real-time control tasks.
As a result, modern vehicles often adopt an MCU + SoC architecture, where:
MCUs typically integrate limited peripherals focused on control tasks, while SoCs support:
SoCs usually rely on external memory and storage, such as DDR and UFS, with capacities reaching hundreds of gigabytes. In contrast, MCUs typically use on-chip Flash and SRAM measured in KB or MB.
In terms of power consumption:
In automotive applications such as intelligent driving and smart cockpits, SoCs may require 20 KDMIPS or more, supporting multi-sensor fusion (e.g., 5 cameras + 5 radars).
| Feature | MCU | SoC |
| Architecture | Simple | Complex, multi-core |
| Startup Time | Very fast | Relatively slow |
| Real-Time Performance | Excellent | Limited |
| Operating System | Bare-metal / RTOS | Linux / QNX / Android |
| Computing Power | Low to medium | Very high |
| Power Consumption | Very low | High |
MCUs are ideal for real-time control and safety-critical tasks, while SoCs excel at high-performance computing and complex system integration.
In modern electric vehicles, both MCUs and SoCs play critical roles—not only in driving and cockpit systems, but also in EV charging control and power management. Components such as charging controllers, BMS units, and communication modules rely on MCUs for real-time control, while SoCs enable connectivity, cloud interaction, and intelligent energy management.
As a company specializing in EV charging solutions, nexwayev works closely with advanced automotive electronics ecosystems. Our products, including type2 ev extension cable, are designed to meet the demands of intelligent electric vehicles. As one of the professional electric vehicle charging cable suppliers, nexwayev supports reliable, safe, and high-performance charging solutions aligned with next-generation vehicle architectures.
The following are our popular EV charging products that you may be interested in. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us, and our specialists will answer within 24 hours.